Prof. Antoni B. Chan
Professor, Dept. of Computer Science
Associate Dean (Research & Postgraduate), College of Computing
Deputy Director, Multimedia Engineering Research Centre (MERC)
BSc MEng Cornell, PhD UC San Diego
SrMIEEE
Video, Image, and Sound Analysis Lab (VISAL)
Department of Computer Science
College of Computing
City University of Hong Kong
Office: Room AC1-G7311, Yeung Kin Man Academic Building (lift 7)
Phone: +852 3442 6509
Fax: +852 3442 0503
Email: abchan at cityu dot edu dot hk
News
- Research Assistant and Technical Assistant positions are available for a project on using ChatGPT in teaching. Details here.
Bio
Dr. Antoni Chan is a Professor at the City University of Hong Kong in the Department of Computer Science. Before joining CityU, he was a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego). He received the Ph.D. degree from UC San Diego in 2008 studying in the Statistical and Visual Computing Lab (SVCL). He received the B.Sc. and M.Eng. in Electrical Engineering from Cornell University in 2000 and 2001. From 2001 to 2003, he was a Visiting Scientist in the Computer Vision and Image Analysis lab at Cornell. In 2005, he was a summer intern at Google in New York City. In 2012, he was the recipient of an Early Career Award from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong SAR, China.
Research Interests [more]
Computer Vision, Surveillance, Machine Learning, Explainable AI (XAI), Pattern Recognition, Computer Audition, Music Information Retrieval, Eye Gaze Analysis
image captioning, object tracking, dynamic textures, motion segmentation, motion analysis, semantic image annotation, image retrieval, crowd counting, probabilistic graphical models, support vector machines, Bayesian regression, Gaussian processes, semantic music annotation and retrieval, music segmentation, feature extraction.
- For more information about my current research projects, please visit my lab website.
- Opportunities for graduate students and research assistants! If you are interested in joining the lab, please check this information. Outstanding non-HK students may also consider applying for the HK PhD fellowship.
Recent Publications [more]
- Threading Keyframe with Narratives: MLLMs as Strong Long Video Comprehenders .
,
In: Intl. Conf. on Learning Representation (ICLR), Rio de Janeiro, to appear 2026. - Adaptive momentum weight averaging reduces initialization noise.
,
Pattern Recognition, 171:112297, Part B, to appear Mar 2026. - GeneQuery: Generalized Gene Expression Prediction from Histology Images via Image-Gene QA.
,
In: Workshop on Machine Learning for Biological and Medical Image Big Data at IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM):5738-5745, Dec 2025. - PUO-Bench: A Panel Understanding and Operation Benchmark with A Privacy-Preserving Framework.
,
In: Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) Track on Datasets and Benchmarks, San Diego, Dec 2025. - Reading an Artist’s Intention from the Composition (RAIC): eye movements and aesthetic experience in Japanese woodblock prints.
,
Frontiers in Psychology, 16:1644803, Nov 2025. - Video Individual Counting for Moving Drones.
,
In: International Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV), Honolulu, Oct 2025 [highlight]. [github] - Temporal Unlearnable Examples: Preventing Personal Video Data from Unauthorized Exploitation by Object Tracking.
,
In: International Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV), Honolulu, Oct 2025. - Explaining Object Detection Through Difference Map.
,
In: International Conf Computer Vision (ICCV) 2025 Workshop on Explainable Computer Vision (eXCV), Honolulu, Oct 2025. - Large language model tokens are psychologically salient.
,
In: Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (CogSci), San Francisco, Jul 2025. - Whose Values Prevail? Bias in Large Language Model Value Alignment.
,
In: Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (CogSci), San Francisco, Jul 2025 [oral]. - Eye movement behavior during mind wandering in older adults.
,
In: Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (CogSci), San Francisco, Jul 2025. - Eye movement analysis with co-clustering of hidden markov models (EMHMM with co-clustering) and with switching hidden Markov Models (EMSHMM).
,
ZL 2019 8 0103423.7, Jun 2025. - DistinctAD: Distinctive Audio Description Generation in Contexts.
,
In: IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2025 (highlight).
Selected Publications [more]
- Understanding the role of eye movement consistency in face recognition and autism through integrating deep neural networks and hidden Markov models.
,
npj Science of Learning, 7:28, Oct 2022. - PRIMAL-GMM: PaRametrIc MAnifold Learning of Gaussian Mixture Models.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 44(6):3197-3211, June 2022 (online 2021). [code] - Wide-Area Crowd Counting: Multi-View Fusion Networks for Counting in Large Scenes.
,
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 130(8):1938-1960, Aug 2022. - On Distinctive Image Captioning via Comparing and Reweighting.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 45(2):2088-2103, Feb 2023 (online 2022). - Kernel-based Density Map Generation for Dense Object Counting.
,
IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 44(3):1357-1370, Mar 2022. - On Diversity in Image Captioning: Metrics and Methods.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 44(2):1035-1049, Feb 2022. - A Generalized Loss Function for Crowd Counting and Localization.
,
In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Jun 2021. [supplemental] - Eye Movement analysis with Hidden Markov Models (EMHMM) with co-clustering.
,
Behavior Research Methods, 53:2473-2486, April 2021. - Visual Tracking via Dynamic Memory Networks.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 43(1):360-374, Jan 2021. [code] - Incorporating Side Information by Adaptive Convolution.
,
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 128:2897-2918, July 2020. - Density-Preserving Hierarchical EM Algorithm: Simplifying Gaussian Mixture Models for Approximate Inference.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 41(6):1323-1337, June 2019. - Beyond Counting: Comparisons of Density Maps for Crowd Analysis Tasks - Counting, Detection, and Tracking.
,
IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), 29(5):1408-1422, May 2019. - Eye Movement Patterns in Face Recognition are Associated with Cognitive Decline in Older Adults.
,
Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 25(6):2200-2207, Dec 2018. - Maximum-Margin Structured Learning with Deep Networks for 3D Human Pose Estimation.
,
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 122(1):149-168, March 2017. - Counting People Crossing a Line using Integer Programming and Local Features.
,
IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), 26(10):1955-1969, Oct 2016. [appendix] - Understanding eye movements in face recognition using hidden Markov models.
,
Journal of Vision, 14(11):8, Sep 2014. - Clustering hidden Markov models with variational HEM.
,
Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR), 15(2):697-747, Feb 2014. [code] - Clustering Dynamic Textures with the Hierarchical EM Algorithm for Modeling Video.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 35(7):1606-1621, Jul 2013. [appendix] - Counting People with Low-Level Features and Bayesian Regression.
,
IEEE Trans. on Image Processing (TIP), 21(4):2170-2177, May 2012. - Generalized Gaussian Process Models.
,
In: IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, Jun 2011. [supplemental] - Layered dynamic textures.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 31(10):1862-1879, Oct 2009. - Modeling, clustering, and segmenting video with mixtures of dynamic textures.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 30(5):909-926, May 2008. - Modeling music as a dynamic texture.
,
IEEE Trans. on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP), 18(3):602-612, Mar 2010. - Supervised learning of semantic classes for image annotation and retrieval.
,
IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 29(3):394-410, Mar 2007.
![]() Google Scholar
Google Scholar
![]() Microsoft Academic
Microsoft Academic
![]() orcid.org/0000-0002-2886-2513
orcid.org/0000-0002-2886-2513
Scopus ID: 14015159100
Recent Project Pages [more]
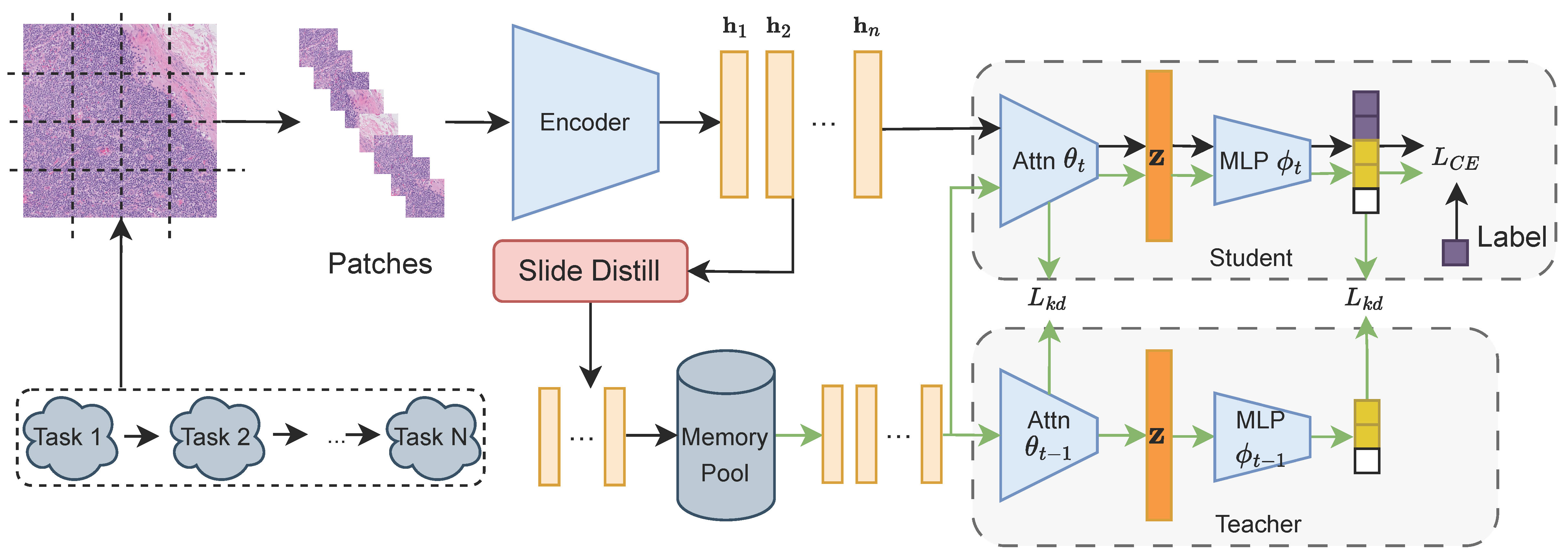
We pinpoint catastrophic forgetting to the attention layers of attention-MIL models for whole-slide images and introduce two remedies: Attention Knowledge Distillation (AKD) to retain attention weights across tasks and a Pseudo-Bag Memory Pool (PMP) that keeps only the most informative patches. Combined, AKD and PMP achieve state-of-the-art continual-learning accuracy while sharply cutting memory usage on diverse WSI datasets.
- , "Advancing Multiple Instance Learning with Continual Learning for Whole Slide Imaging." In: IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2025 (highlight).
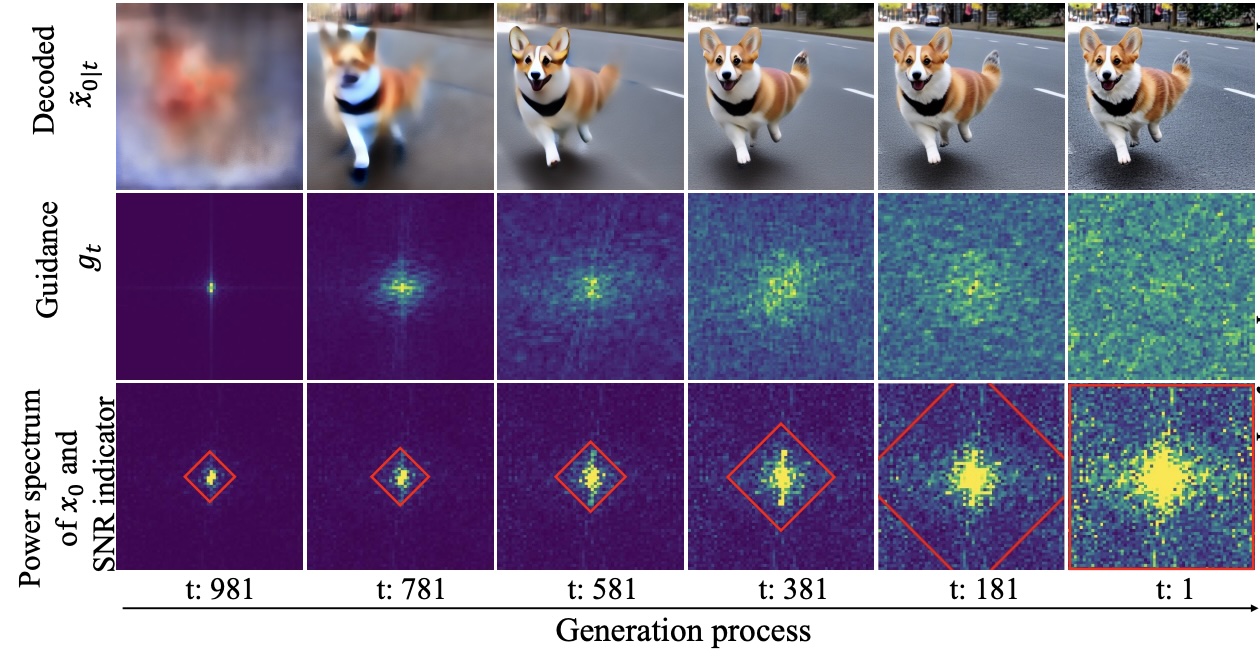
We introduce a novel fine-tuning free approach that employs progressive Frequency truncation to refine the guidance of Diffusion models for universal editing tasks (FreeDiff).
- , "FreeDiff: Progressive Frequency Truncation for Image Editing with Diffusion Models." In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milano, Oct 2024. [supplemental | github]
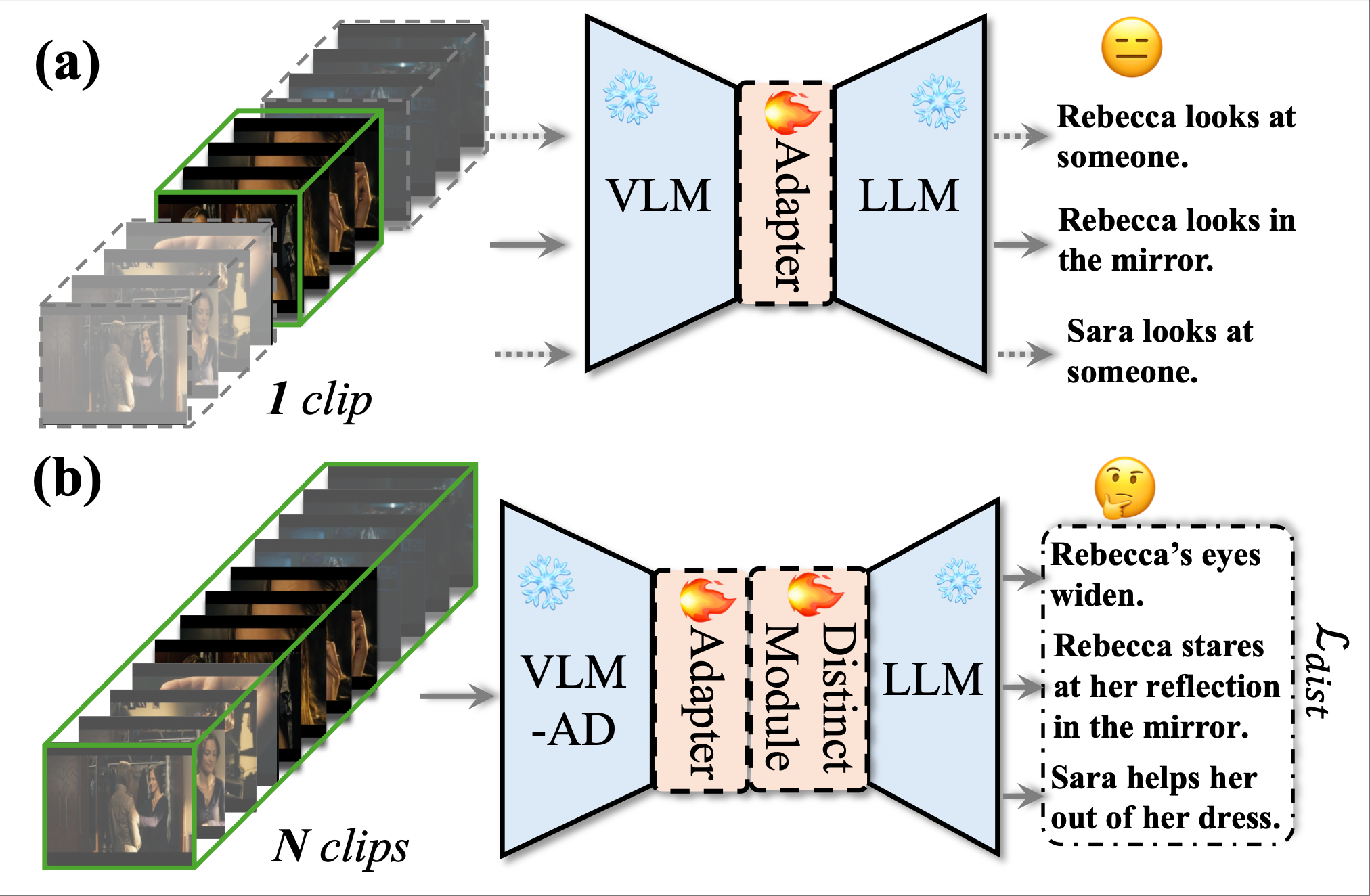
We propose a two-stage framework DistinctAD for automatically generating audio descriptions in movies or tv series. DistinctAD targets at generating distinctive and interesting ADs in similar contextual video clips.
- , "DistinctAD: Distinctive Audio Description Generation in Contexts." In: IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2025 (highlight).
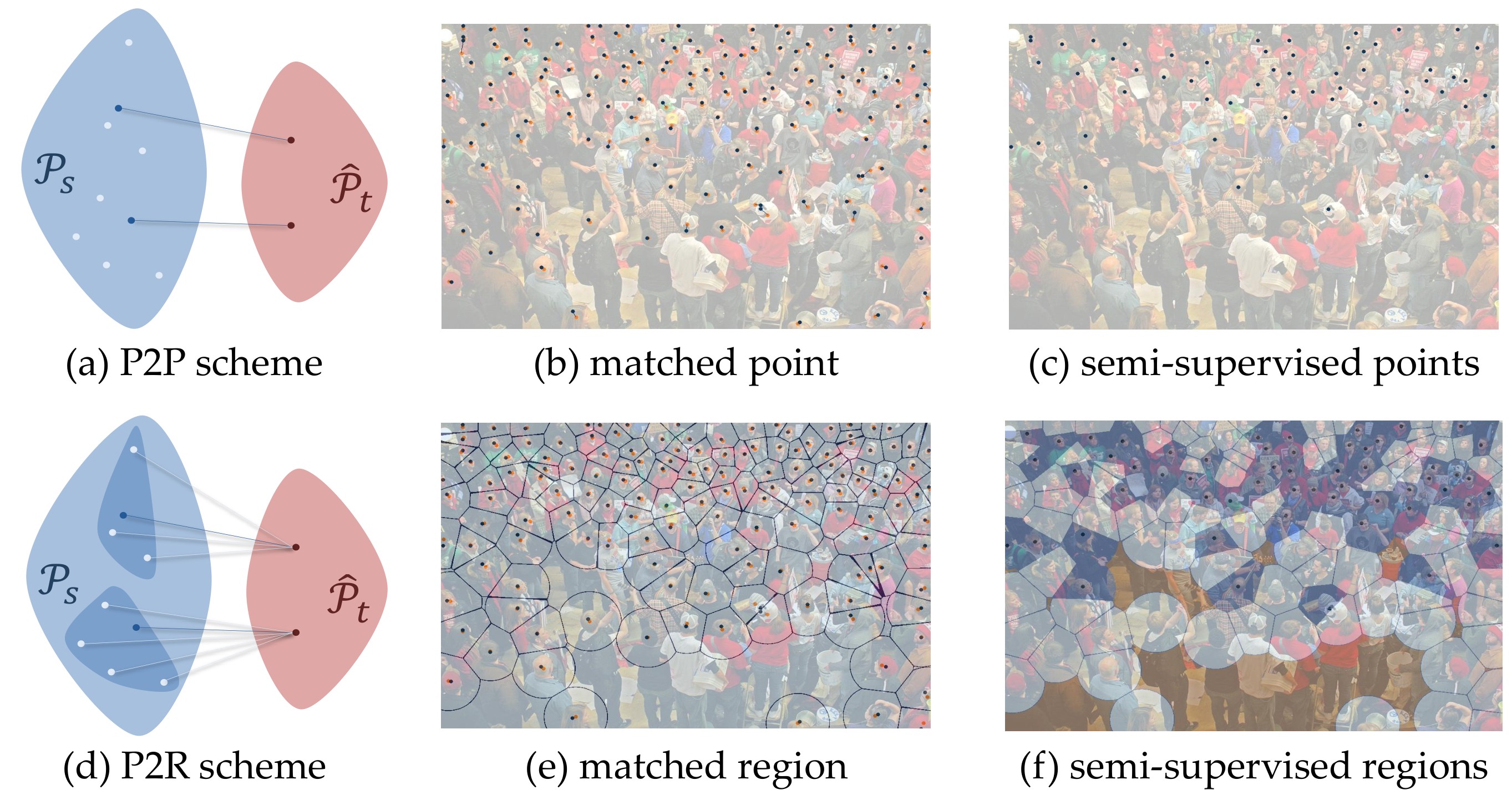
We introduce a Point-to-Region (P2R) loss to address the over-activation and pseudo-label propagation issues inherent in semi-supervised crowd counting. By replacing pixel-level matching with region-level supervision, P2R suppresses background noise and achieves state-of-the-art results with significantly higher training stability.
- , "Point-to-Region Loss for Semi-Supervised Point-Based Crowd Counting." In: IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2025 (highlight).
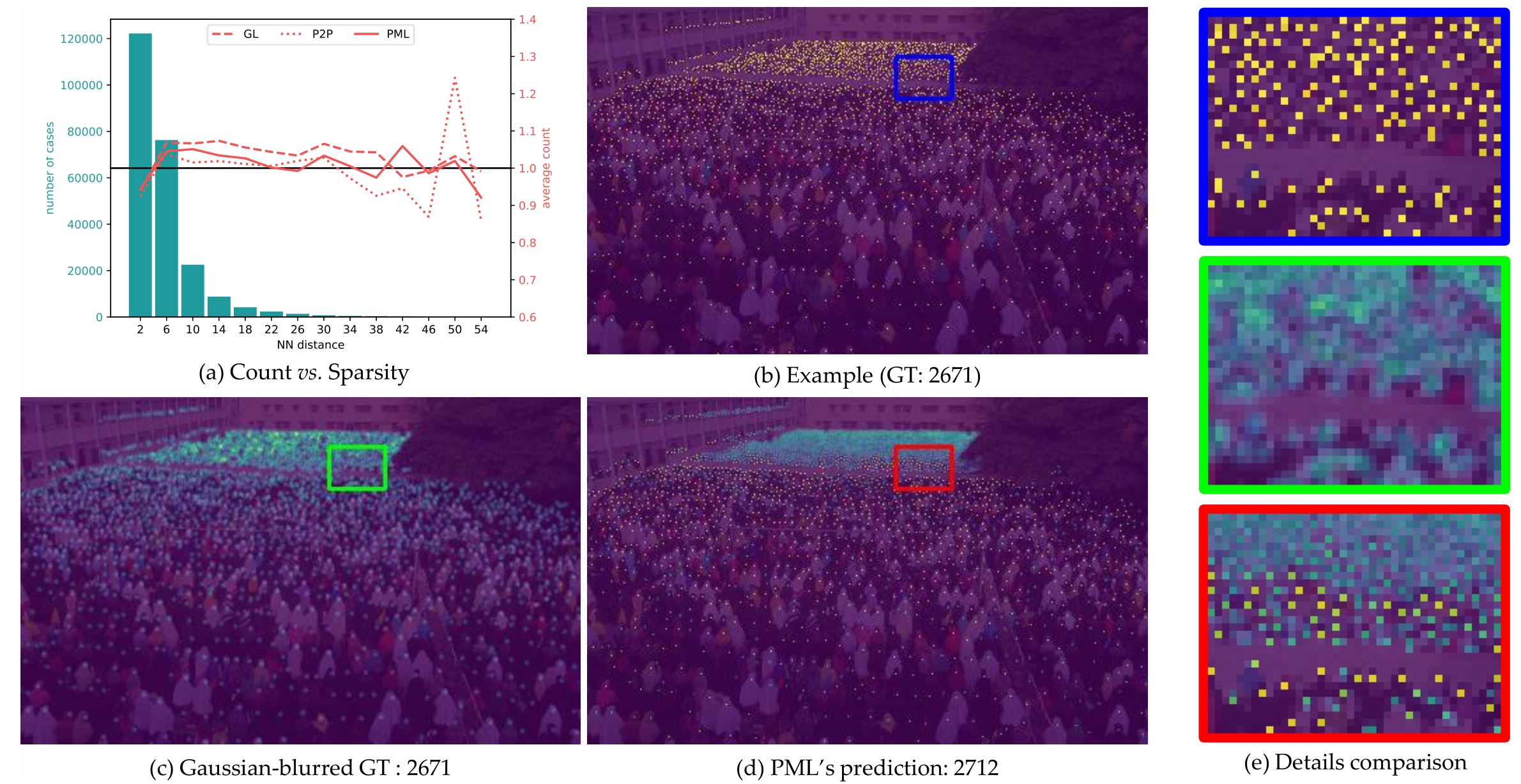
We propose the Proximal Mapping Loss (PML), a theoretically grounded framework that discards the unrealistic “non-overlap” assumption common in crowd counting. By leveraging proximal operators from convex optimization, PML accurately recovers density in highly congested scenes where severe occlusions and overlapping objects are prevalent.
- , "Proximal Mapping Loss: Understanding Loss Functions in Crowd Counting & Localization." In: Intl. Conf. on Learning Representations (ICLR), Singapore, Apr 2025.
Recent Datasets and Code [more]
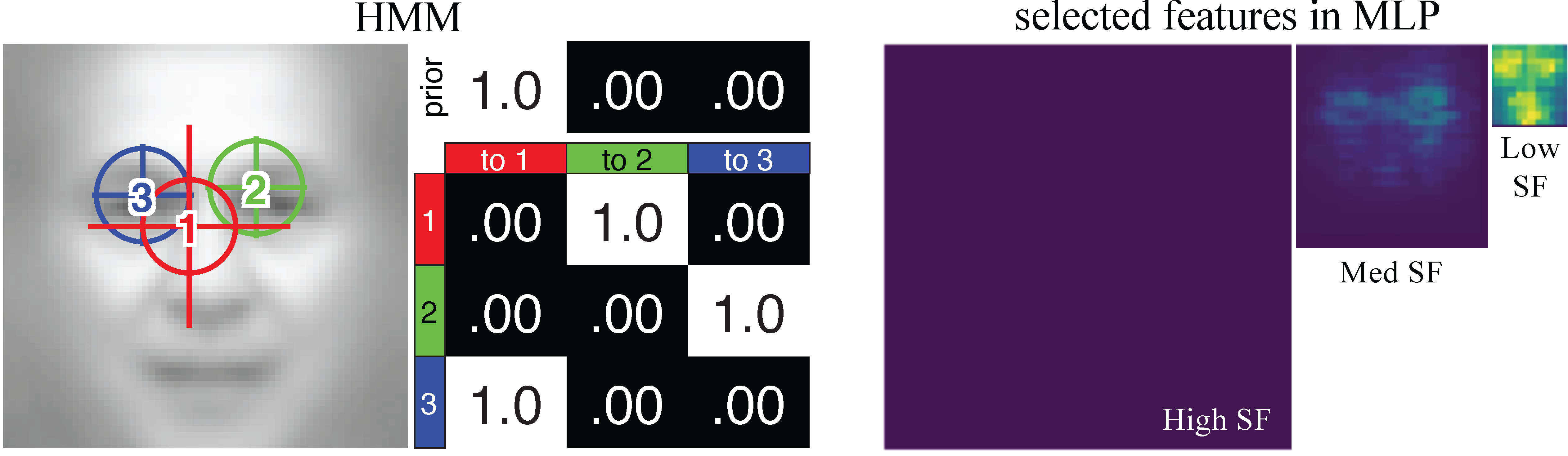
Modeling Eye Movements with Deep Neural Networks and Hidden Markov Models (DNN+HMM)
This is the toolbox for modeling eye movements and feature learning with deep neural networks and hidden Markov models (DNN+HMM).
- Files: download here
- Project page
- If you use this toolbox please cite:
Understanding the role of eye movement consistency in face recognition and autism through integrating deep neural networks and hidden Markov models.
,
npj Science of Learning, 7:28, Oct 2022.
Dolphin-14k: Chinese White Dolphin detection dataset
A dataset consisting of Chinese White Dolphin (CWD) and distractors for detection tasks.
- Files: Google Drive, Readme
- Project page
- If you use this dataset please cite:
Chinese White Dolphin Detection in the Wild.
,
In: ACM Multimedia Asia (MMAsia), Gold Coast, Australia, Dec 2021.
Crowd counting: Zero-shot cross-domain counting
Generalized loss function for crowd counting.
- Files: github
- Project page
- If you use this toolbox please cite:
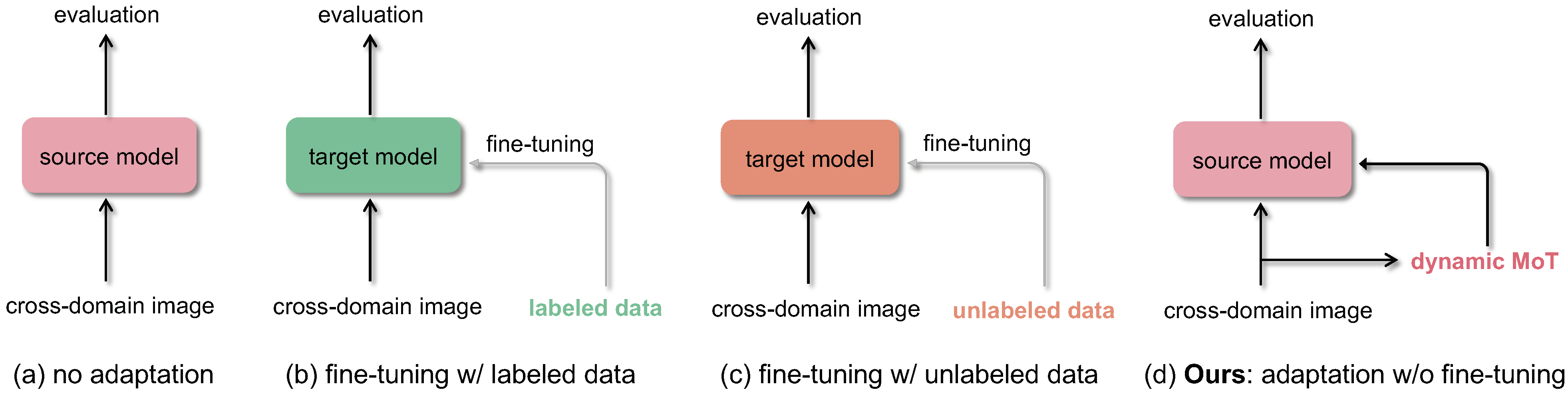
Dynamic Momentum Adaptation for Zero-Shot Cross-Domain Crowd Counting.
,
In: ACM Multimedia (MM), Oct 2021.
CVCS: Cross-View Cross-Scene Multi-View Crowd Counting Dataset
Synthetic dataset for cross-view cross-scene multi-view counting. The dataset contains 31 scenes, each with about ~100 camera views. For each scene, we capture 100 multi-view images of crowds.
- Files: Google Drive
- Project page
- If you use this dataset please cite:
Cross-View Cross-Scene Multi-View Crowd Counting.
,
In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR):557-567, Jun 2021.
Crowd counting: Generalized loss function
Generalized loss function for crowd counting.
- Files: github
- Project page
- If you use this toolbox please cite:
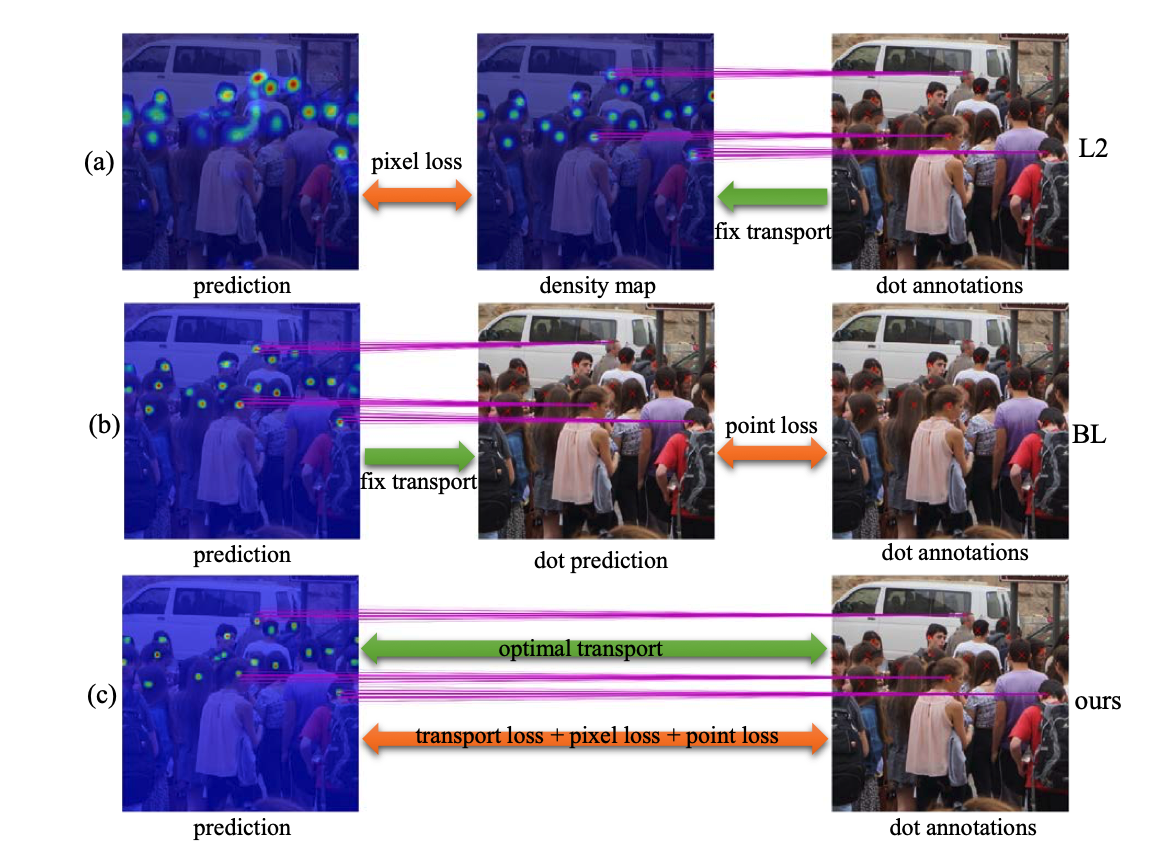
A Generalized Loss Function for Crowd Counting and Localization.
,
In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Jun 2021.
Teaching
- CS 5495 – Explainable AI — 2025A.
- CS 5487 – Machine Learning: Principles & Practice (postgraduate) — 2012A-2026B.
- CS 5489 – Machine Learning: Algorithms & Applications (postgraduate) — 2020B-2025B.
- GE1361 – Digital Literacy: New Technologies, Society, and You — 2025B-2026B.
- CS 6487 – Topics in Machine Learning (postgraduate) — 2019B.
- CS 4487 – Machine Learning (undergraduate) — 2015A-2018A.
- GE 2326 – Probability in Action: From the Unfinished Game to the Modern World — 2015B-2017B.
- GE 1319 – Interdisciplinary Research for Smart Professionals — 2013B-2017B.
- CS 5301 – Computer Programming — 2012A-2014A.
- CS 2363 – Computer Programming — 2009A-2011A.
- CS 3306 (B) – Contemporary Programming Methods in Java — 2010B.
- CS 4380 (B) – Web 2.0 Technologies — 2011B, 2012B.
- Multimedia Subject Group leader
- Research Mentoring Scheme Coordinator
- Final Year Project Coordinator (2016-2022)
- MSCS Project and Guided Study Coordinator (2016-2022)
- BScCM Deputy Programme Leader (2020-2022)
Service
- Associate Editor, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2023-now)
- Action Editor, Transactions on Machine Learning Research (2022-now)
- Guest Editor, Special Issue on “Applications of artificial intelligence, computer vision, physics and econometrics modelling methods in pedestrian traffic modelling and crowd safety”, Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies (2022-23)
- Senior Area Editor, IEEE Signal Processing Letters (2016-2020)
- Associate Editor, IEEE Signal Processing Letters (2014-2016)
- Conference Area Chair
- CVPR – 2020, 2023, 2026
- ICCV – 2015, 2017, 2019, 2021, 2025 (Lead AC)
- ECCV – 2022, 2024, 2026
- NeurIPS – 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024, 2025 (top 10%)
- ICML – 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024, 2025, 2026
- ICLR – 2021, 2023, 2024, 2025, 2026
- ICPR – 2020
- Pacific Graphics – 2018
- Conference Senior PC
- AAAI – 2021, 2022
- IJCAI – 2019-20
- Conference Program Committees
- CVPR – 2012-2019, 2021, 2022, 2024, 2025
- ICCV – 2011, 2013, 2023
- ECCV – 2012, 2014, 2016, 2018
- ACCV – 2011, 2014, 2016
- ICML – 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2018, 2019, 2020
- NIPS – 2015, 2017, 2018, 2019
- ICLR – 2022
- Siggraph (tertiary)- 2018
- Journal Reviewing
- IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)
- IEEE Trans. on Image Processing (TIP)
- Intl. Journal Computer Vision (IJCV)
- IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT)
- IEEE Trans. on Neural Networks (TNN)
- IEEE Trans. on Multimedia
- IEEE Trans. Intelligent Transportation Systems
- Grant Reviewing
- A*STAR-JST
- Organized Events
- CogSci 2022 Hong Kong Meetup & Symposium: Computational Approaches to Psychological Research, Aug 2022.
Awards and Honors
- Top 2% Most Highly Cited Researchers (Ioannidis et al. 2019. Plos Biology)
- The President’s Award, City University of Hong Kong, 2016.
- Early Career Award, Research Grants Council of Hong Kong, 2012.
- NSF IGERT Fellowship: Vision and Learning in Humans and Machines, UCSD, 2006-07.
- Outstanding Teaching Assistant Award, ECE Department, UCSD, 2005-06.
- Office of the President Award, UCSD, 2003.
- Henry G. White Scholorship, Cornell University, 2001.
- Knauss M. Engineering Scholorship, Cornell University, 2001.
- GTE Fellowship, Cornell University, 2001.
Mailing Address:
Prof. Antoni Chan,
Department of Computer Science,
City University of Hong Kong,
Tat Chee Avenue,
Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong.
©IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.