About
Welcome to the Video, Image, and Sound Analysis Lab (VISAL) at the City University of Hong Kong! The lab is directed by Prof. Antoni Chan in the Department of Computer Science.
Our main research activities include:
- Computer Vision, Surveillance
- Machine Learning, Pattern Recognition
- Computer Audition, Music Information Retrieval
- Eye Gaze Analysis
For more information about our current research, please visit the projects and publication pages.
Opportunities for graduate students and research assistants – if you are interested in joining the lab, please check this information.
Latest News [more]
- [May 27, 2025]
Congratulations to Chenyang for defending her thesis!
- [Feb 11, 2025]
Congratulations to Jiuniu for defending his thesis!
- [Apr 9, 2024]
Congratulations to Qiangqiang for defending his thesis!
- [Jun 16, 2023]
Congratulations to Hui for defending her thesis!
Recent Publications [more]
- Adaptive momentum weight averaging reduces initialization noise.
,
Pattern Recognition, 171:112297, Part B, to appear Mar 2026. - PUO-Bench: A Panel Understanding and Operation Benchmark with A Privacy-Preserving Framework.
,
In: Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) Track on Datasets and Benchmarks, San Diego, Dec 2025. - Reading an Artist’s Intention from the Composition (RAIC): eye movements and aesthetic experience in Japanese woodblock prints.
,
Frontiers in Psychology, 16:1644803, Nov 2025. - Video Individual Counting for Moving Drones.
,
In: International Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV), Honolulu, Oct 2025 [highlight]. [github] - Temporal Unlearnable Examples: Preventing Personal Video Data from Unauthorized Exploitation by Object Tracking.
,
In: International Conf. Computer Vision (ICCV), Honolulu, Oct 2025. - Explaining Object Detection Through Difference Map.
,
In: International Conf Computer Vision (ICCV) 2025 Workshop on Explainable Computer Vision (eXCV), Honolulu, Oct 2025. - Large language model tokens are psychologically salient.
,
In: Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (CogSci), San Francisco, Jul 2025. - Whose Values Prevail? Bias in Large Language Model Value Alignment.
,
In: Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (CogSci), San Francisco, Jul 2025 [oral].
Recent Project Pages [more]
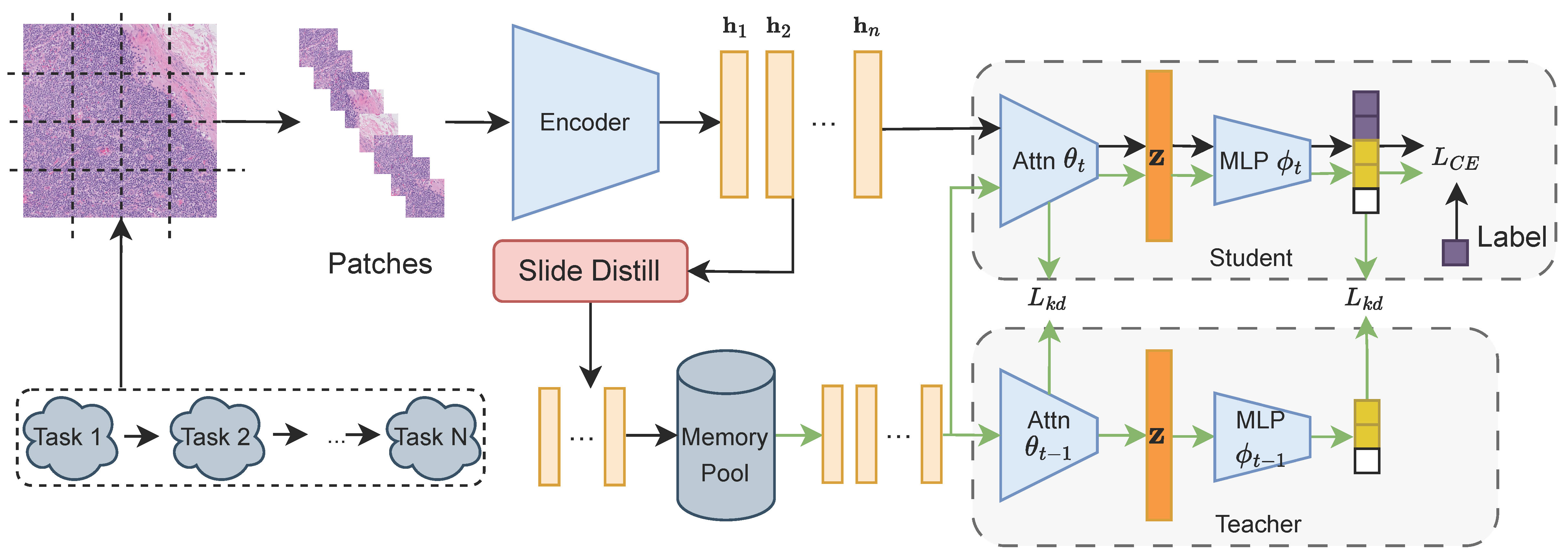
We pinpoint catastrophic forgetting to the attention layers of attention-MIL models for whole-slide images and introduce two remedies: Attention Knowledge Distillation (AKD) to retain attention weights across tasks and a Pseudo-Bag Memory Pool (PMP) that keeps only the most informative patches. Combined, AKD and PMP achieve state-of-the-art continual-learning accuracy while sharply cutting memory usage on diverse WSI datasets.
- , "Advancing Multiple Instance Learning with Continual Learning for Whole Slide Imaging." In: IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2025 (highlight).
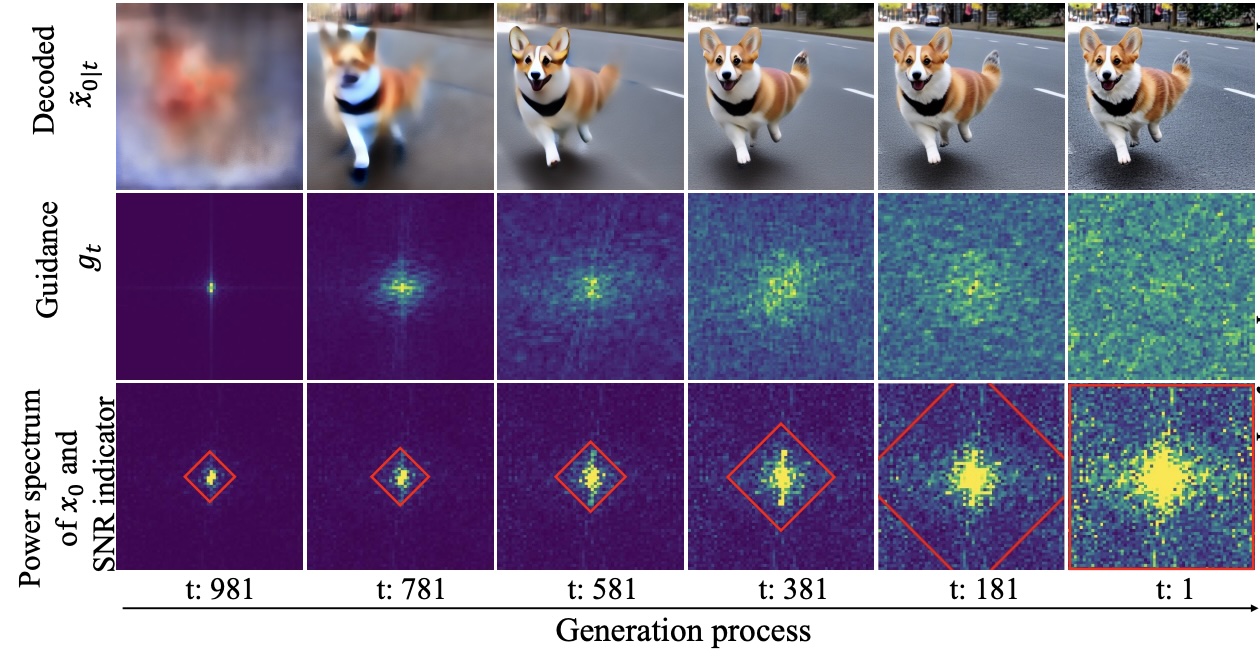
We introduce a novel fine-tuning free approach that employs progressive Frequency truncation to refine the guidance of Diffusion models for universal editing tasks (FreeDiff).
- , "FreeDiff: Progressive Frequency Truncation for Image Editing with Diffusion Models." In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milano, Oct 2024. [supplemental | github]
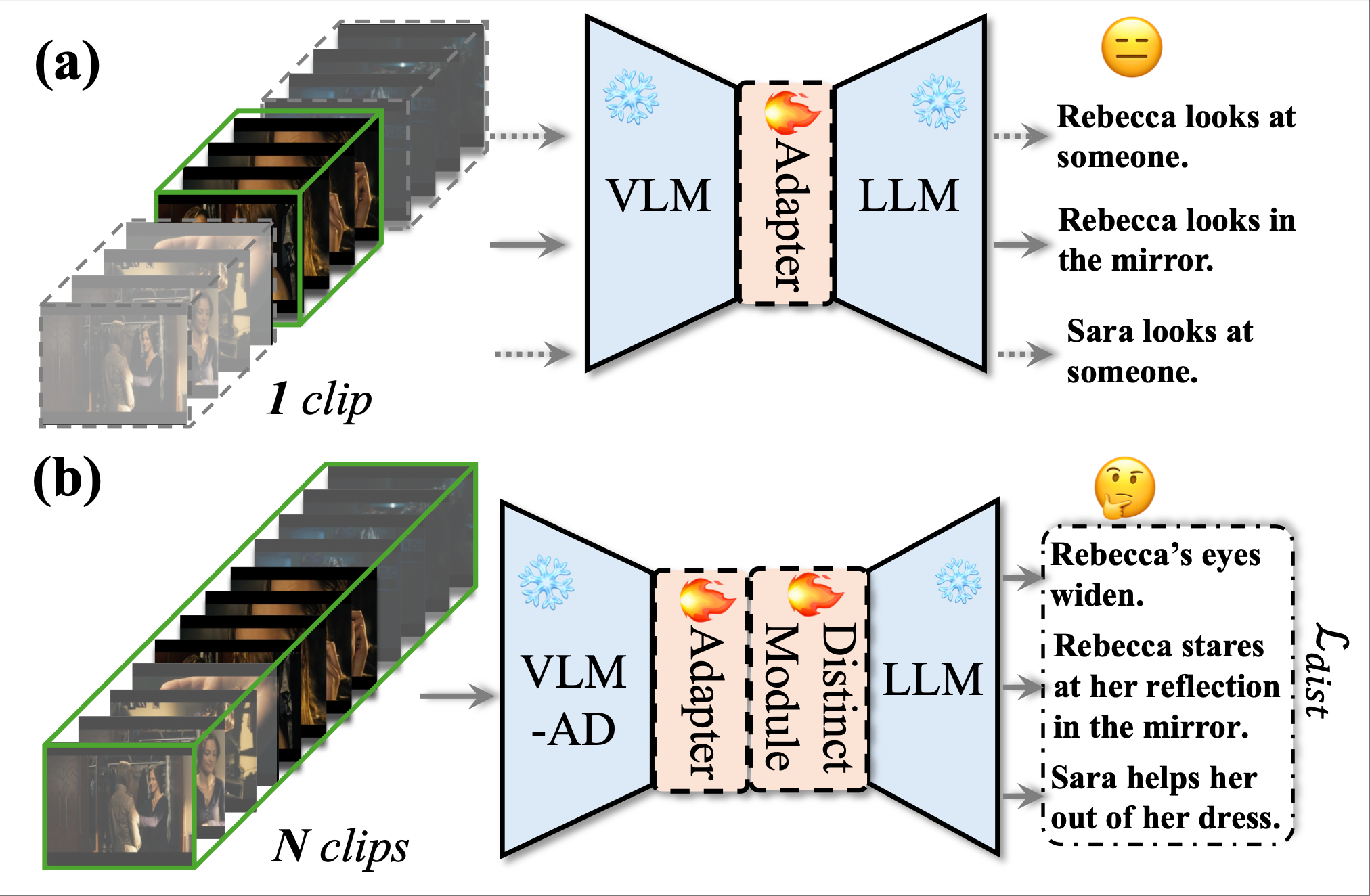
We propose a two-stage framework DistinctAD for automatically generating audio descriptions in movies or tv series. DistinctAD targets at generating distinctive and interesting ADs in similar contextual video clips.
- , "DistinctAD: Distinctive Audio Description Generation in Contexts." In: IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2025 (highlight).
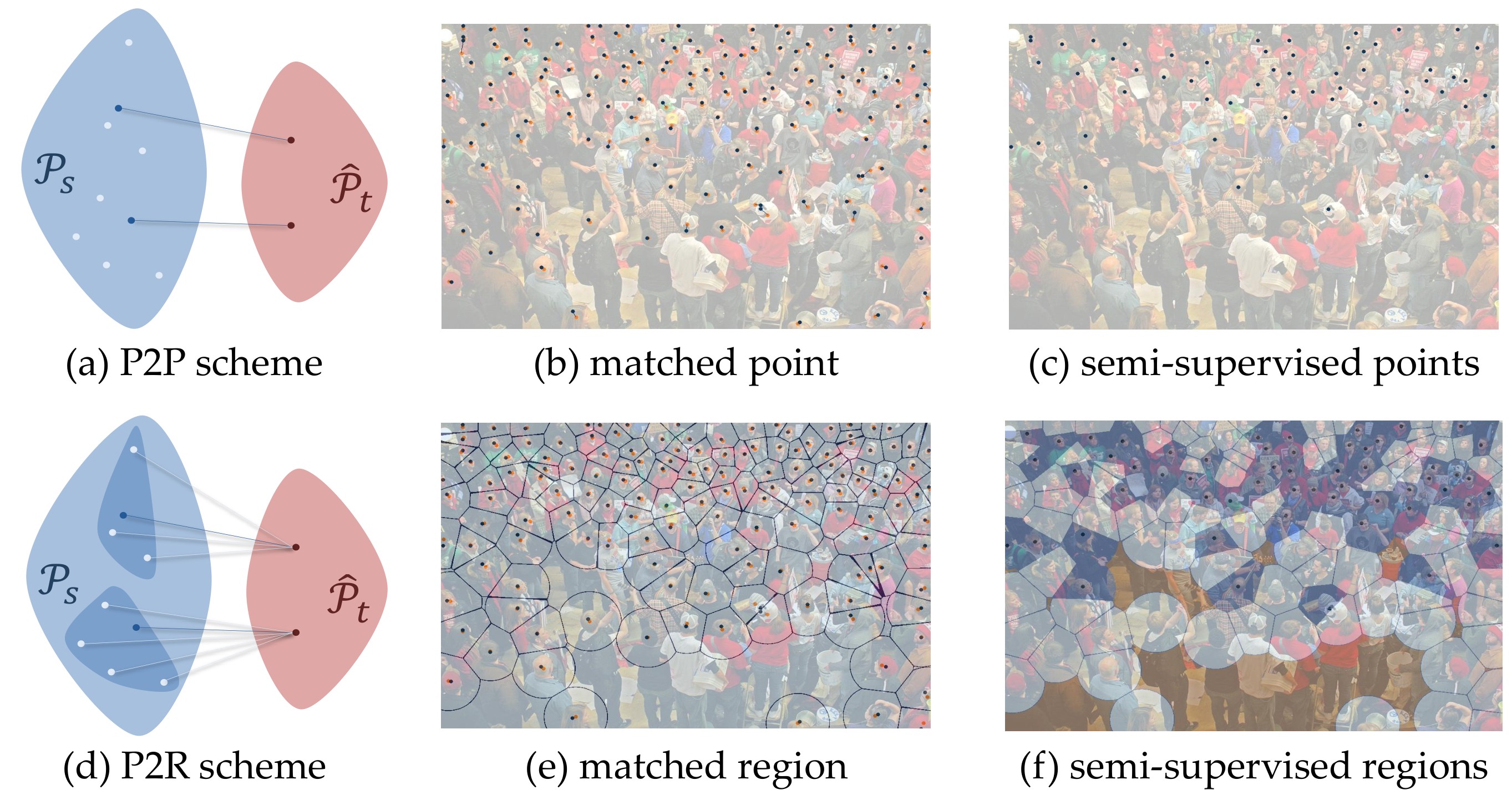
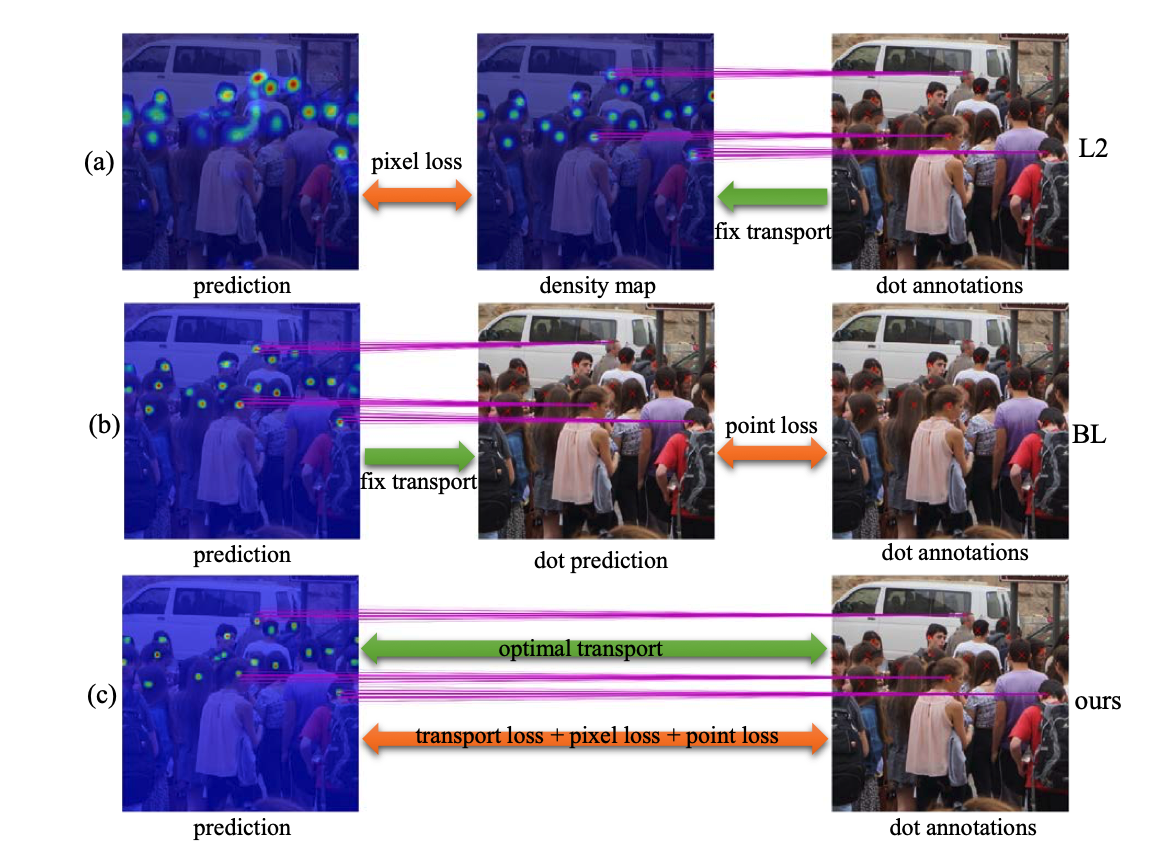
We introduce a Point-to-Region (P2R) loss to address the over-activation and pseudo-label propagation issues inherent in semi-supervised crowd counting. By replacing pixel-level matching with region-level supervision, P2R suppresses background noise and achieves state-of-the-art results with significantly higher training stability.
- , "Point-to-Region Loss for Semi-Supervised Point-Based Crowd Counting." In: IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), June 2025 (highlight).
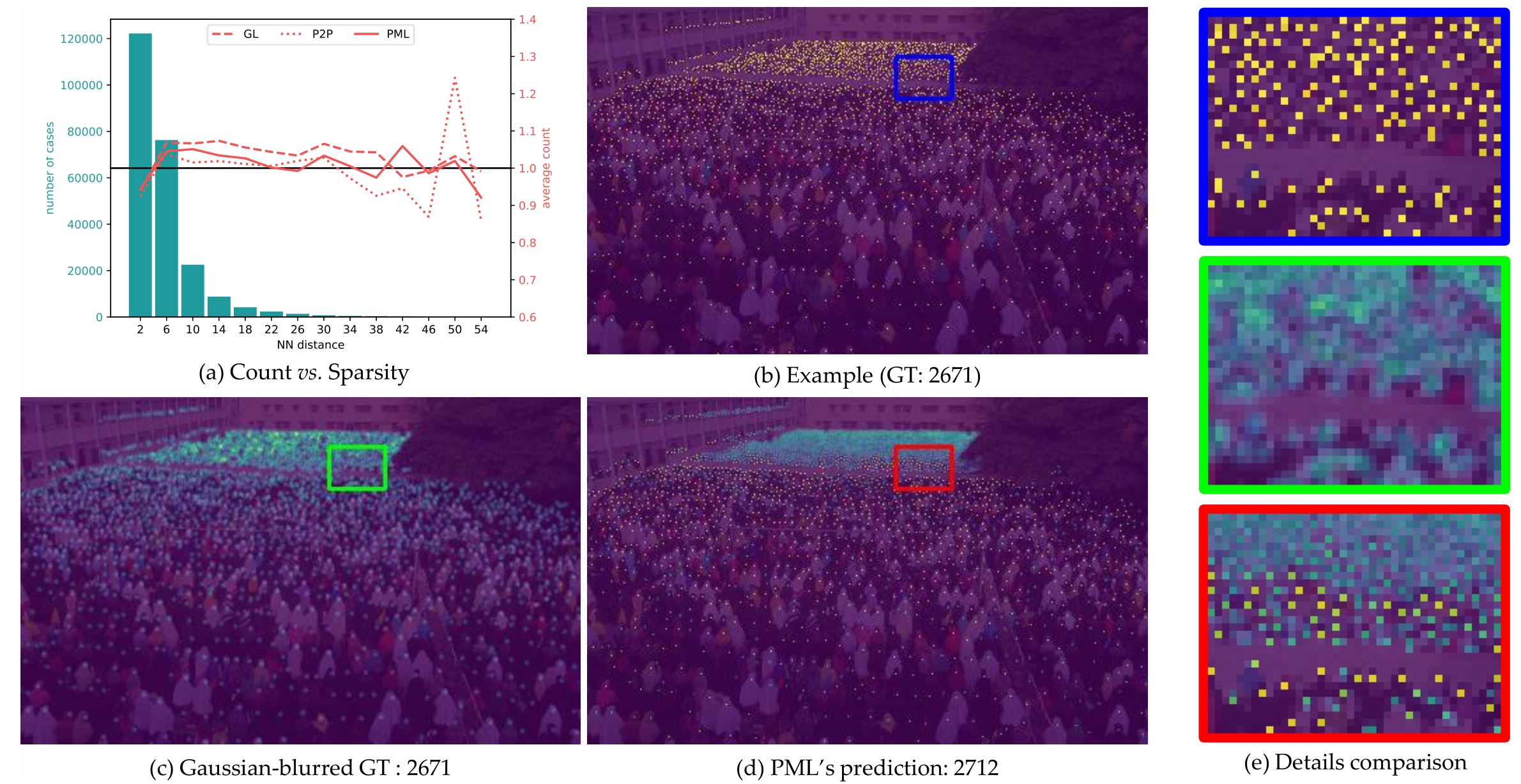
We propose the Proximal Mapping Loss (PML), a theoretically grounded framework that discards the unrealistic “non-overlap” assumption common in crowd counting. By leveraging proximal operators from convex optimization, PML accurately recovers density in highly congested scenes where severe occlusions and overlapping objects are prevalent.
- , "Proximal Mapping Loss: Understanding Loss Functions in Crowd Counting & Localization." In: Intl. Conf. on Learning Representations (ICLR), Singapore, Apr 2025.
Recent Datasets and Code [more]
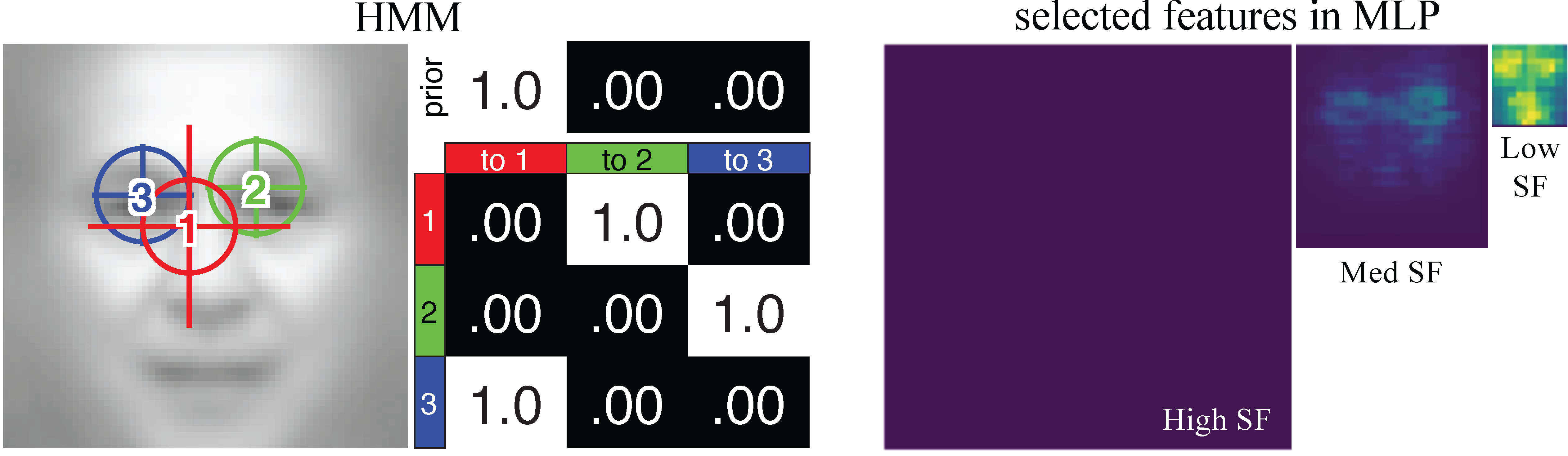
Modeling Eye Movements with Deep Neural Networks and Hidden Markov Models (DNN+HMM)
This is the toolbox for modeling eye movements and feature learning with deep neural networks and hidden Markov models (DNN+HMM).
- Files: download here
- Project page
- If you use this toolbox please cite:
Understanding the role of eye movement consistency in face recognition and autism through integrating deep neural networks and hidden Markov models.
,
npj Science of Learning, 7:28, Oct 2022.
Dolphin-14k: Chinese White Dolphin detection dataset
A dataset consisting of Chinese White Dolphin (CWD) and distractors for detection tasks.
- Files: Google Drive, Readme
- Project page
- If you use this dataset please cite:
Chinese White Dolphin Detection in the Wild.
,
In: ACM Multimedia Asia (MMAsia), Gold Coast, Australia, Dec 2021.
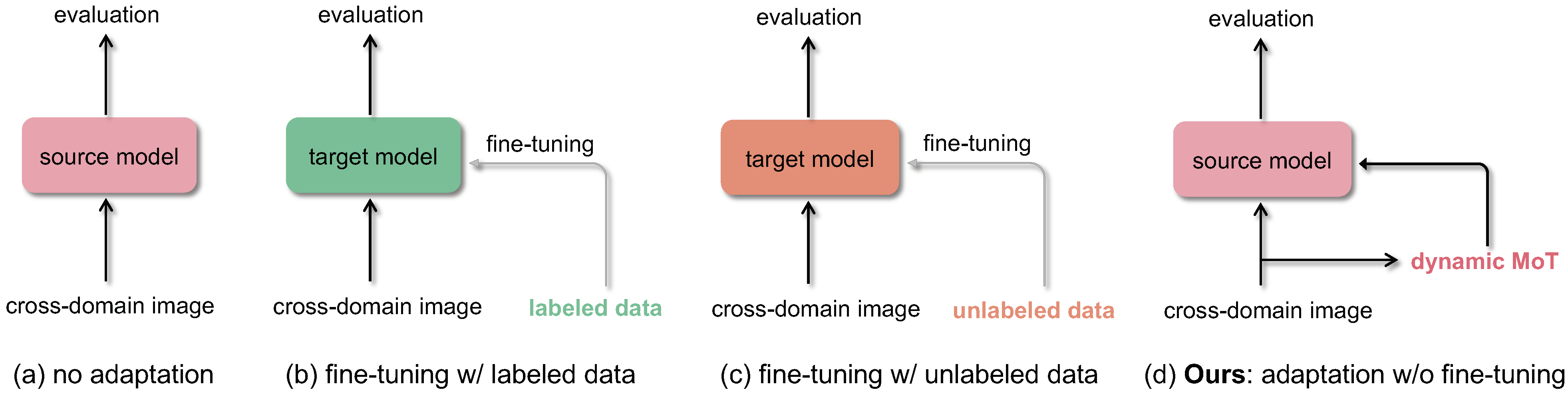
Crowd counting: Zero-shot cross-domain counting
Generalized loss function for crowd counting.
- Files: github
- Project page
- If you use this toolbox please cite:
Dynamic Momentum Adaptation for Zero-Shot Cross-Domain Crowd Counting.
,
In: ACM Multimedia (MM), Oct 2021.
CVCS: Cross-View Cross-Scene Multi-View Crowd Counting Dataset
Synthetic dataset for cross-view cross-scene multi-view counting. The dataset contains 31 scenes, each with about ~100 camera views. For each scene, we capture 100 multi-view images of crowds.
- Files: Google Drive
- Project page
- If you use this dataset please cite:
Cross-View Cross-Scene Multi-View Crowd Counting.
,
In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR):557-567, Jun 2021.
Crowd counting: Generalized loss function
Generalized loss function for crowd counting.
- Files: github
- Project page
- If you use this toolbox please cite:
A Generalized Loss Function for Crowd Counting and Localization.
,
In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Jun 2021.