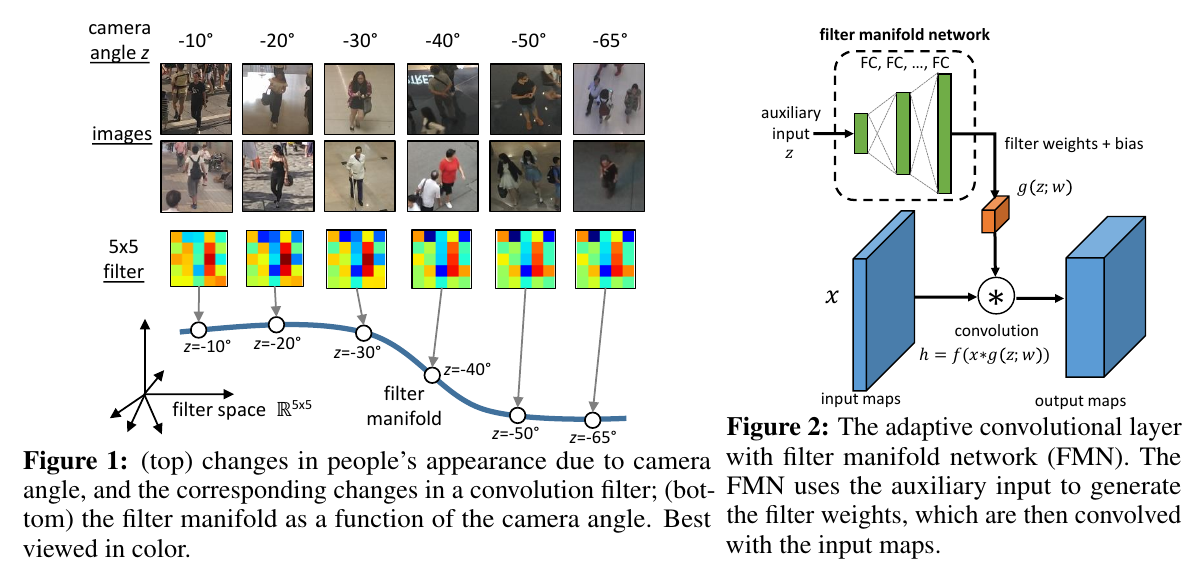
Computer vision tasks often have side information available that is helpful to solve the task. For example, for crowd counting, the camera perspective (e.g., camera angle and height) gives a clue about the appearance and scale of people in the scene. While side information has been shown to be useful for counting systems using traditional hand-crafted features, it has not been fully utilized in counting systems based on deep learning. In order to incorporate the available side information, we propose an adaptive convolutional neural network (ACNN), where the convolution filter weights adapt to the current scene context via the side information. In particular, we model the filter weights as a low-dimensional manifold within the high-dimensional space of filter weights. The filter weights are generated using a learned “filter manifold” sub-network, whose input is the side information. With the help of side information and adaptive weights, the ACNN can disentangle the variations related to the side information, and extract discriminative features related to the current context (e.g. camera perspective, noise level, blur kernel parameters). We demonstrate the effectiveness of ACNN incorporating side information on 3 tasks: crowd counting, corrupted digit recognition, and image deblurring. Our experiments show that ACNN improves the performance compared to a plain CNN with a similar number of parameters. Since existing crowd counting datasets do not contain ground-truth side information, we collect a new dataset with the ground-truth camera angle and height as the side information.
Selected Publications
- Incorporating Side Information by Adaptive Convolution.
,
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 128:2897-2918, July 2020. - Incorporating Side Information by Adaptive Convolution.
,
In: Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, Dec 2017. [supplemental]
Demos/Results/Dataset
