Previous works show that a better density map representation can improve the performance of crowd counting. In this paper, we investigate learning the density map representation through an unbalanced optimal transport problem, and propose a generalized loss function to learn density maps for crowd counting and localization. We prove that pixel-wise L2 loss and Bayesian loss are special cases and suboptimal solutions to our proposed loss function. A perspective-guided transport cost function is further proposed to better handle the perspective transformation in crowd images. Since the predicted density will be pushed toward annotation positions, the density map prediction will be sparse and can naturally be used for localization. Finally, the proposed loss outperforms other losses on four large-scale datasets for counting, and achieves the best localization performance on NWPU-Crowd and UCF-QNRF.
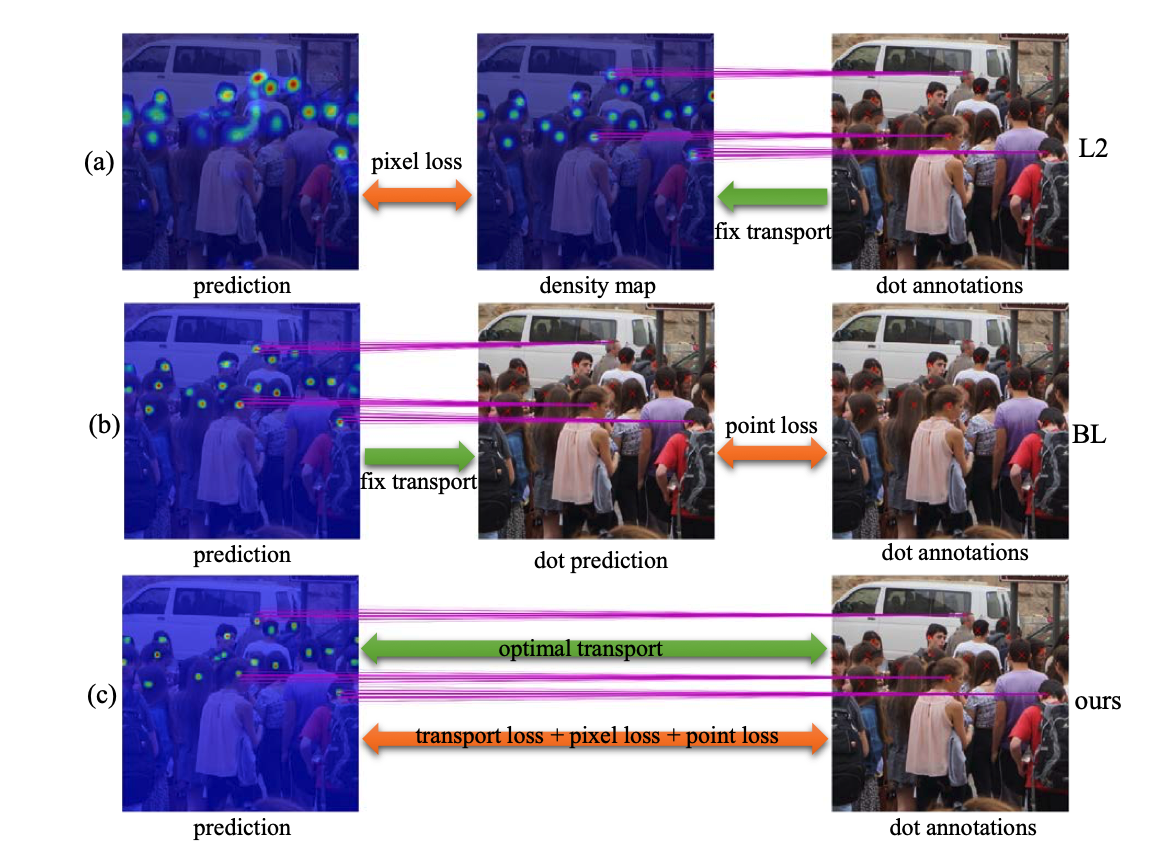
The relationships among the losses is shown in the figure above: (a) L2 loss generates density map as the supervision and uses a pixel-wise loss function. (b) Bayesian loss (BL) computes an aggregated dot prediction and uses a point-wise loss function. We show that L2 and BL are related to an optimal transport problem using a suboptimal transport matrix. (c) Our proposed loss is based on unbalanced optimal transport, where the transport cost is fully minimized and both the pixel-wise and point-wise losses are considered.
Selected Publications
,
In: IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Jun 2021. [supplemental]
